When it comes to creating content on WordPress, you are presented with two primary editing options: the Block Editor (also known as Gutenberg) and the Classic Editor. Both of these tools allow you to create and manage your website’s content, but they offer different approaches and user experiences.
What is the Block Editor (Gutenberg)?
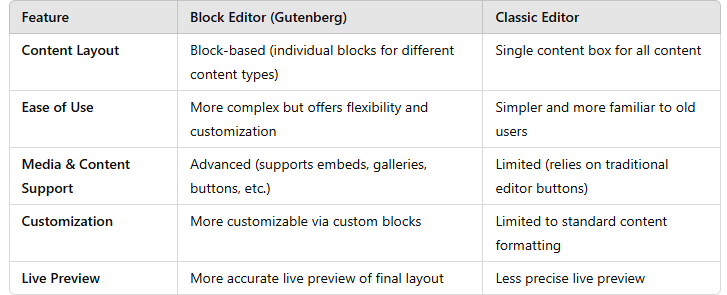
The Block Editor is the default content editor in WordPress as of version 5.0, released in December 2018. It’s a modern, block-based editor that introduces a new approach to creating content. Instead of a single content box like in traditional editors, the Block Editor breaks down your content into “blocks,” where each block represents a different type of content (text, images, headings, galleries, etc.).
Key Features of the Block Editor:
- Block-Based Layout: Each piece of content (text, image, video, etc.) is treated as an individual block, making it easier to manipulate and rearrange them.
- Drag-and-Drop Functionality: You can easily rearrange blocks by dragging and dropping them in the editor.
- Rich Media Support: You can add complex content like buttons, columns, embeds, and more without needing extra plugins.
- Live Preview: The Block Editor gives you a more accurate preview of how your content will look on the live site.
- Extensibility: Developers can create custom blocks for more functionality.
What is the Classic Editor?
The Classic Editor is the traditional WordPress content editor that was used before the introduction of the Block Editor (Gutenberg). It provides a familiar interface to users who are accustomed to the old editor style, which is essentially a single content area for writing text, adding media, and inserting links.
Key Features of the Classic Editor:
- Simple and Familiar Interface: It retains the classic WordPress layout with a single WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) text editor, similar to old word processors like Microsoft Word.
- Less Complex: The Classic Editor doesn’t rely on blocks, so it’s easier for users who prefer a more straightforward, no-frills approach to content creation.
- Supports TinyMCE: The TinyMCE editor, which powers the Classic Editor, offers useful features like a toolbar, font customization, alignment tools, and the ability to add media.
- Compatibility: It’s often preferred by users who have been using WordPress for a long time and are reluctant to adapt to the new block-based system.
Block Editor vs. Classic Editor: Key Differences
How to Install the Block Editor
The Block Editor comes pre-installed in all versions of WordPress starting from WordPress 5.0. Therefore, if you are using a modern version of WordPress, the Block Editor is already activated by default.
If for any reason the Block Editor is disabled on your site or you need to reinstall it, here’s how you can do it:
- Ensure WordPress is Up-to-Date: Make sure your WordPress installation is running version 5.0 or later.
- Check for Block Editor Activation:
- Go to the WordPress dashboard.
- Click on Posts or Pages and click Add New to create a new post or page.
- If the Block Editor is active, you should see a page layout with various content blocks such as text, image, and heading options.
- Install the Gutenberg Plugin (Optional): If you’re using an older version of WordPress and don’t have the Block Editor yet, you can manually install the Gutenberg plugin:
- Go to Plugins > Add New.
- Search for Gutenberg and click Install Now.
- After installation, click Activate.
Once activated, Gutenberg will be your default content editor for all posts and pages.
How to Install the Classic Editor
If you prefer the Classic Editor over the Block Editor, WordPress makes it easy to install the Classic Editor plugin and switch back. Here’s how you can do it:
- Install the Classic Editor Plugin:
- Go to your WordPress dashboard.
- Navigate to Plugins > Add New.
- Search for Classic Editor.
- Click Install Now next to the Classic Editor plugin by WordPress Contributors.
- After installation, click Activate.
- Configure the Classic Editor Settings:
- Once activated, go to Settings > Writing.
- Under the Default editor for all users section, you can choose between the Block Editor and Classic Editor.
- Select Classic Editor as your default option.
- You can also allow users to switch between editors if you have multiple authors or contributors.
Now, when you create new posts or pages, the Classic Editor will be the default editor.
