Definition of Accounting
Accounting is a systematic recording day to day business transaction is called as accounting.
Accounting is the process of identifying, recording, classifying and reporting information on financial transactions in a systematic manner for the purpose of providing financial information for decision making.
Identifying:
In accounting, the process begins with identifying financial transactions. This involves recognizing and gathering information about any economic events or activities that have a financial impact on an organization.
Recording:
Once financial transactions are identified, they are recorded in a systematic and organized manner. This typically involves entering data into accounting journals or software.
Classifying:
After recording, transactions are classified or categorized into various accounts. This step involves allocating each transaction to the appropriate account, such as revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity.
Reporting:
Accounting goes beyond just recording transactions; it involves preparing and presenting financial reports
Types of Accounts
There are basically three types of Accounts maintained for transactions
- Personal Account
- Real Account
- Nominal Account
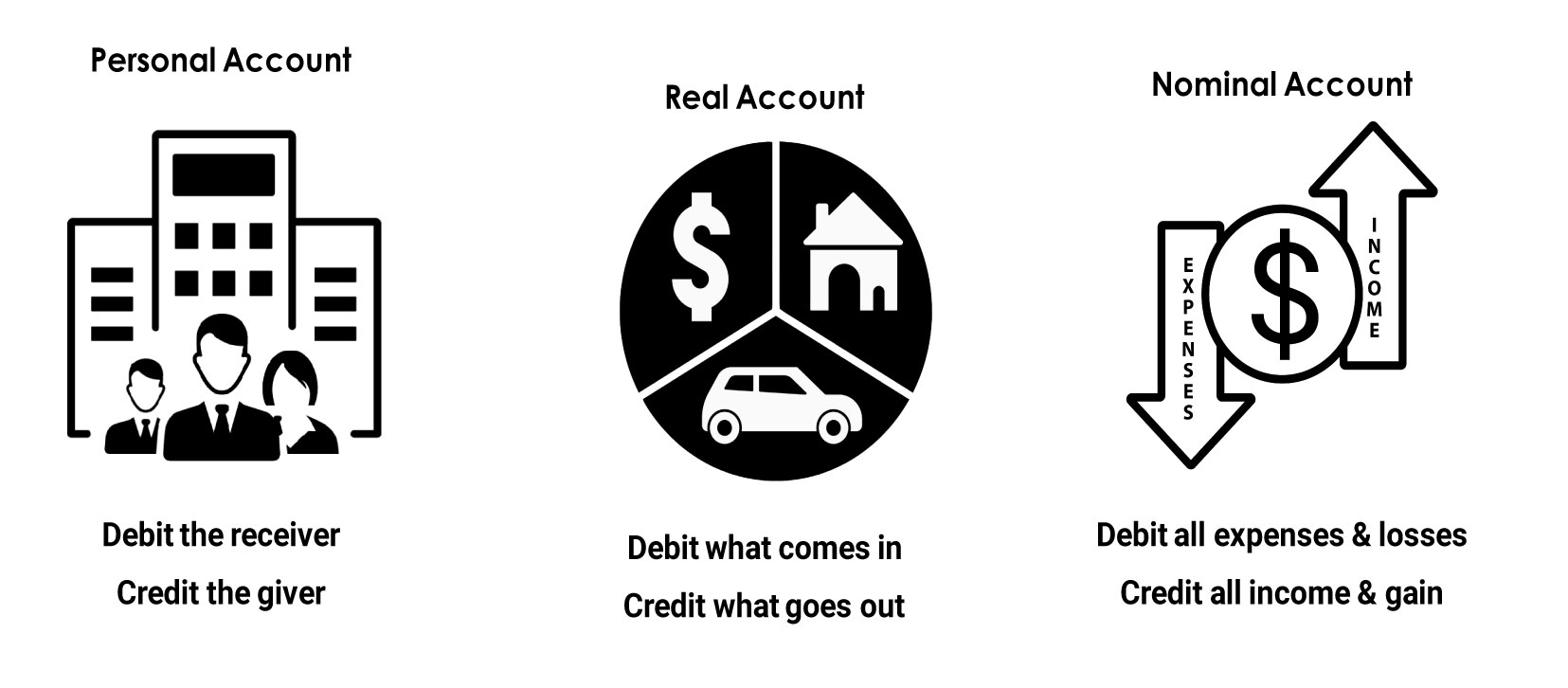
1. Personal Account:
Any individual person or any firms or any company or a bank is considered in a Personal account.
For example:-
- Rajesh Singh
- Munna Enterprise
- Wipro Pvt Ltd
- PNB Bank
- Capital etc.
Rules -:
- Debit the receiver
- Credit the giver
Debit the receiver, credit the giver: When a business receives something, such as cash or goods, it is recorded as a debit in the accounting system. When a business gives something, such as cash or goods, it is recorded as a credit in the accounting system.
2. Real Account:
Account of any physical things. The cash account or goods account are examples of Real account.
For example:-
- Cash
- Land
- Building
- Furniture
- Computer etc.
Rules :-
- Debit what comes in
- Credit what goes out
Debit what comes in, credit what goes out: When there is an inflow of assets or an increase in liabilities, it is recorded as a debit in the accounting system. When there is an outflow of assets or a decrease in liabilities, it is recorded as a credit in the accounting system.
3. Nominal Account:
Account of any invisible things that means that things are in terms of cash are examples of Nominal account.
For example:-
- Discount
- Commission
- Salary
- wages
- Freight etc.
Rules :-
- Debit expenses and losses
- Credit incomes and gains
Debit expenses and losses, credit incomes and gains: This rule states that expenses and losses are recorded as debits in the accounting system, while incomes and gains are recorded as credits.